A novel method has the capability to precisely identify the author of unknown texts, particularly news articles
15 Jan 2024
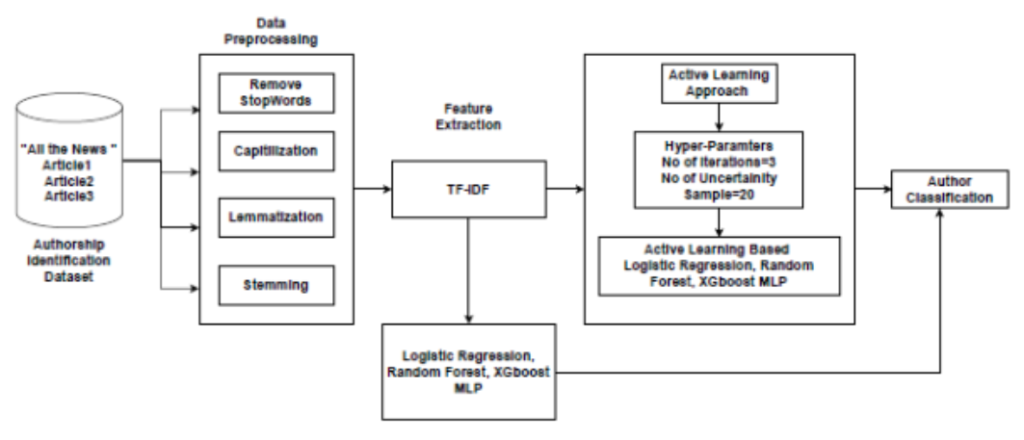
This study tackles the challenge of figuring out who wrote anonymous text, like online articles, in an age when there is more text out there than ever before. We came up with a smart system that can accurately pinpoint the author of unknown texts, even when there is very little information to go on. We use a technique called “Active Learning” which means the system keeps learning and getting better as it goes along. This is super helpful because it can help us make sense of all the anonymous content floating around. We also came up with a new way to do this using computer programs that learn from the text. We tested our approach using a big dataset of news articles, and we found that our method worked really well. In fact, one of our models, AL-XGB, did a fantastic job on one set of articles, while another model, AL-LR, did well on a different set, and AL-MLP performed best on yet another set. This means that our approach can be useful for finding out who wrote what, even when we do not know who the author is in the first place.
This research holds significant importance as it tackles the growing issue of identifying anonymous content creators, particularly in the era of abundant textual data. By employing Active Learning, it streamlines and enhances the authorship identification process, offering a more efficient and precise means of attributing authors to texts, even when information is limited. This capability has broad applications, spanning content moderation, plagiarism detection, cybersecurity, and more, making it highly relevant in diverse domains. Moreover, the study’s utilization of machine and deep learning models, along with TF-IDF, demonstrates innovation in applying advanced technologies to real-world challenges. Additionally, the research’s recognition of varying model performance across different text subsets underscores the need for customized approaches. Overall, this research provides practical solutions for verifying authorship and preserving content integrity in the digital age, addressing a pressing issue in our information-driven society.
Read the full paper: https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3310813
