Research
As the national university, we champion and support innovative research that addresses the country’s most pressing challenges.
30 Apr 2024
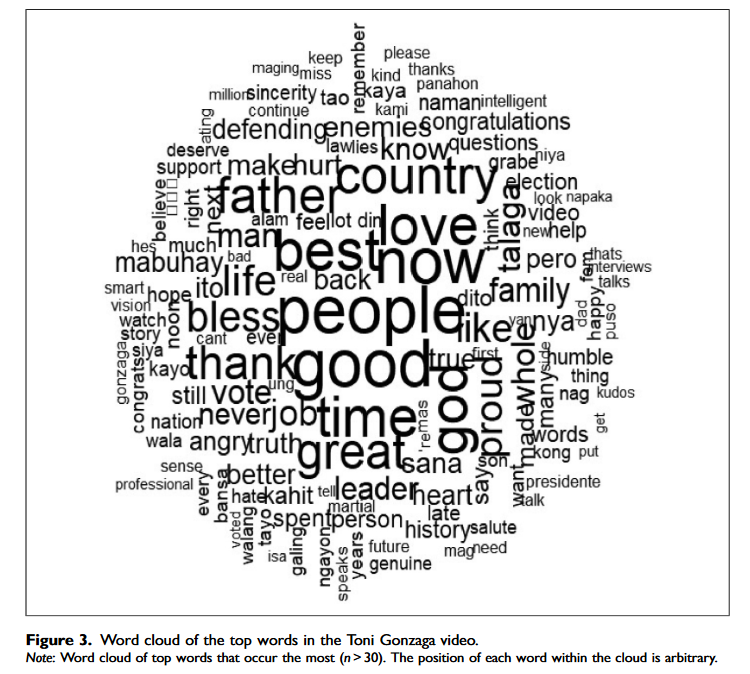
The framework of being (agi) and becoming (kaagian) from Western Visayan poetry enriches our understanding of “queerness” without western/Eurocentric theorizing
This paper analyzes poetry written by self-identified Agi (Panayanon indigenous gay identity) using the concept of power called gahum as...
Read More29 Apr 2024
People with lower levels of education are more likely to trust in the television as an institution
This study is significant as it aims to provide empirical evidence on the celebrity culture, i.e. the pervasive fascination of...
Read More26 Apr 2024
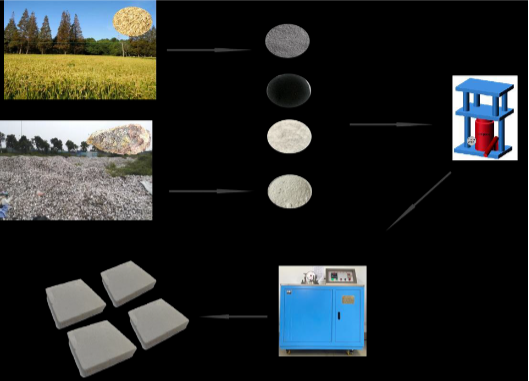
Oyster shell and rice husk can be turned into low-cost building materials with antimicrobial properties
The development of green and low-cost functional building materials is increasingly becoming one of the primary goals in the construction...
Read More11 Apr 2024
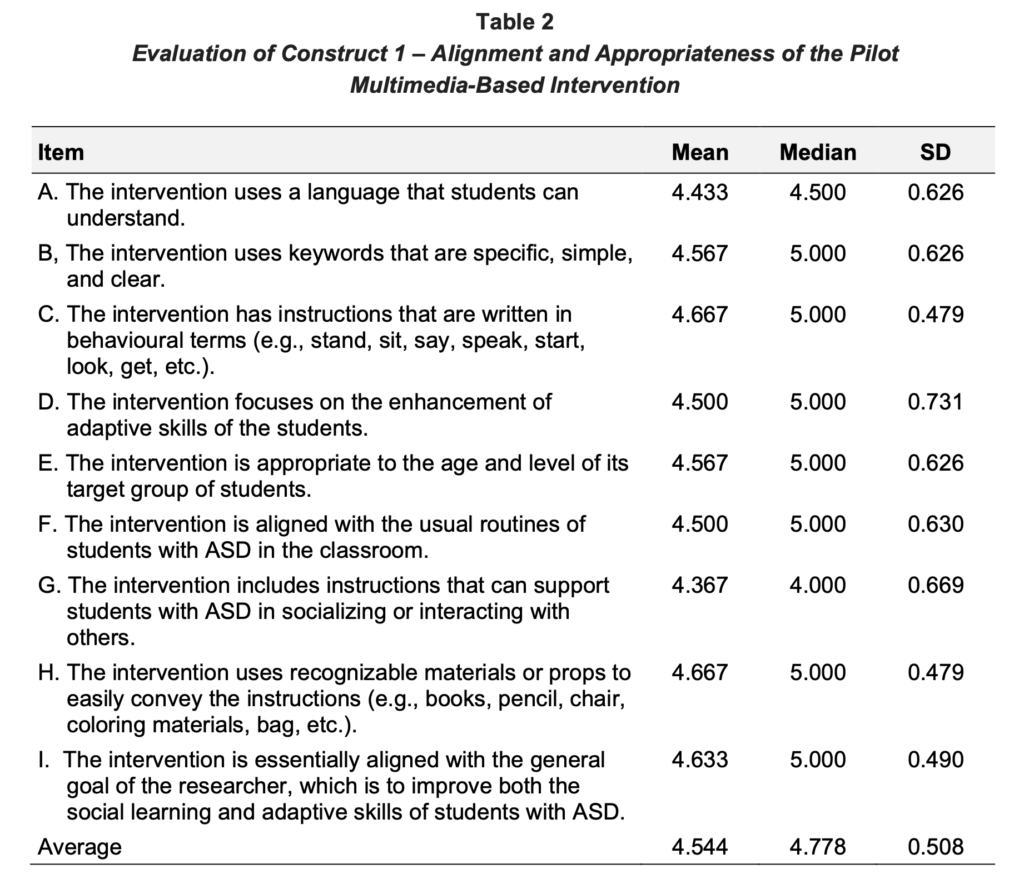
A multimedia-based intervention has the potential to improve social learning and adaptive skills of students with autism spectrum disorder
An evaluation was conducted to examine the potential effectiveness of a multimedia-based intervention, with the participation of 30 Filipino public...
Read More05 Apr 2024
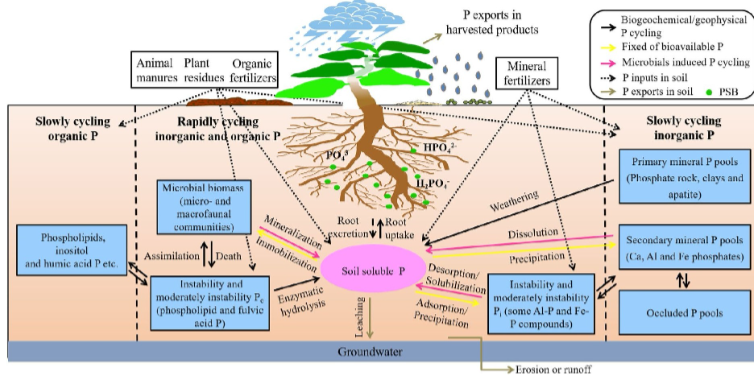
Research highlights the functions of bacteria that dissolve phosphate and make phosphorus, which can improve crop yields, available in soil
Bioavailable phosphorus (P) is critical for improving crop yields to meet the raising food demand driven by an increasing human...
Read More02 Apr 2024
Philippine presidents have used different strategies in their Labor Day speeches to appeal to audiences
How do Philippine presidents frame their messages about labor and migration, especially during Labor Day? Studying this research domain is...
Read More26 Mar 2024
ChatGPT, although a promising tool that can complement nutrition education, still has substantial limitations such as incorrect responses
The field of health and medical sciences has witnessed a surge of published research exploring the applications of ChatGPT. However,...
Read More20 Mar 2024
Living alone increases level of anxiety; no link between anxiety and time spent with smartphones
This quantitative research was completed with the primary objective of determining whether anxiety and digital phenotypes might be regarded as...
Read More13 Mar 2024
False information about the unsuccessful rollout of Dengvaxia® has made it harder for the public to value vaccination programs
The study aimed to identify various issues related to the Dengvaxia® (a dengue vaccine) controversy and link these issues with...
Read More08 Mar 2024
Violence Against Women desks in barangays lack equipment and officers who can carry out responsibilities effectively
The Violence Against Women (VAW) Desk, established by virtue of Republic Act 9710 or the Magna Carta of Women, is...
Read More08 Mar 2024
Research analyzes the shortcomings in Catholic schools’ responses to sex abuse cases that occurred under their watch
This article focuses on sex abuse and abuse of power in Catholic schools in the Philippines.
I used a theological...
Read More06 Mar 2024
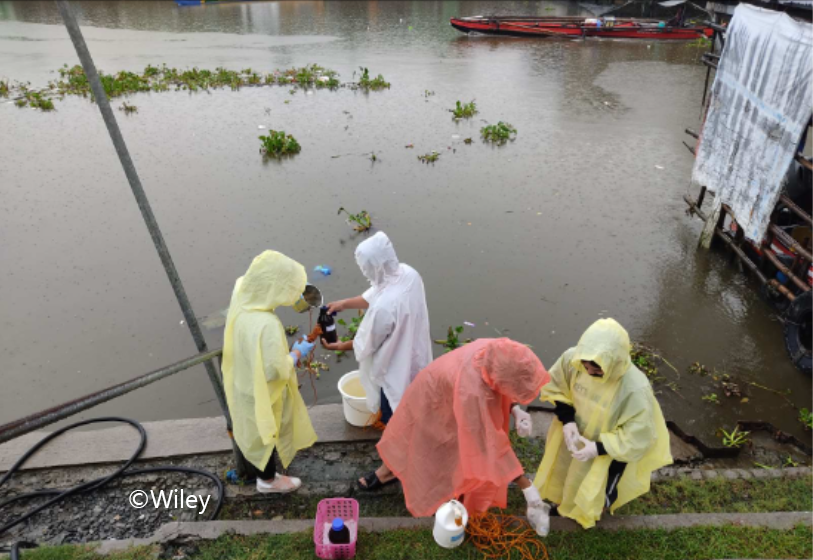
High concentrations of endocrine-disrupting compounds from domestic wastewater and industrial effluents have been detected for the first time in major rivers in Mega Manila
Endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) are environmental contaminants of emerging concern due to their possible health effects on humans and aquatic...
Read More