Pharmacy students are skilled in nonverbal communication and language use, but less confident in developing and managing treatment plans
29 Jul 2024
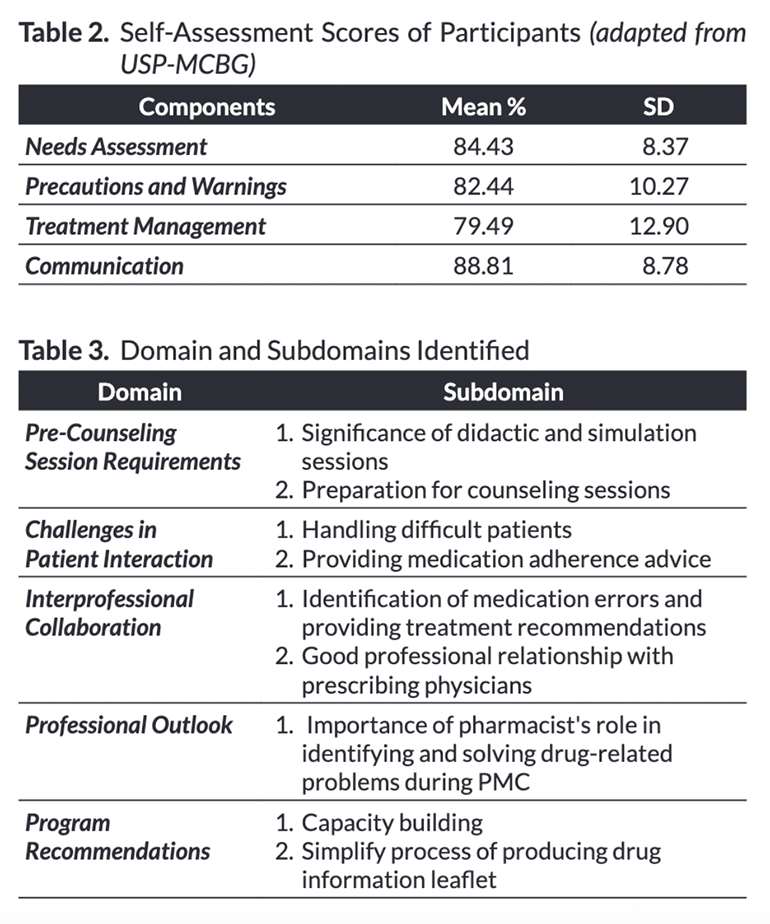
Pharmacists are in a unique position to provide important medication information, prevent errors, and help improve patient outcomes. Patient medication counseling (PMC) is integral in medication therapy management of pharmacists. The objective of the study is to describe the students’ perceptions of a university-led patient medication counseling program implemented in a patient medication counseling course. The study employs a qualitative study design with a total population sampling of forty-two (42) ClinPharm 176 BS Pharmacy students. A self-evaluation adapted from the United States Pharmacopeia medication counseling behavior guidelines (USP-MCBG) scale was performed. A synthesis session was conducted utilizing a semi-structured questionnaire. The data was analyzed using measures of central tendency and thematic analysis. Forty-two students answered the USP-MCBG scale and participated in the synthesis session. Participants rated highest in communication (88.81±8.78) and lowest in treatment management (79.49±12.90) suggesting that the students were better equipped in displaying effective nonverbal behaviors and using appropriate language but were least confident in developing and managing treatment plans. There were five main domains on how the students evaluated the course and the PMC program which include pre-counseling session requirements, challenges in patient interaction, interprofessional collaboration, professional outlook, and program recommendations. A university-led PMC program is effective in providing training for student pharmacists to identify and provide recommendations on medication therapy problems and practice interprofessional collaboration. It is recommended to continue the student training in the PMC program and to integrate this in the student internship program to evaluate the skills development of students during their clinical rotations. The results of the study will help in improving the provision of patient medication counseling by student pharmacists and pharmacists altogether. It will also contribute to the improvement of didactic sessions to equip student pharmacists with the appropriate set of skills and knowledge to counsel patients in real-world setting.
Authors: Frances Lois U. Ngo, Camille Francesca T. Cadag and Jan Redmong V. Ordoñez (Department of Pharmacy, College of Pharmacy, University of the Philippines Manila)
Read the full paper: https://actamedicaphilippina.upm.edu.ph/index.php/acta/article/view/8335
