Researchers pioneer the use of topological data analysis for Filipino Sign Language alphabet recognition
05 Dec 2025
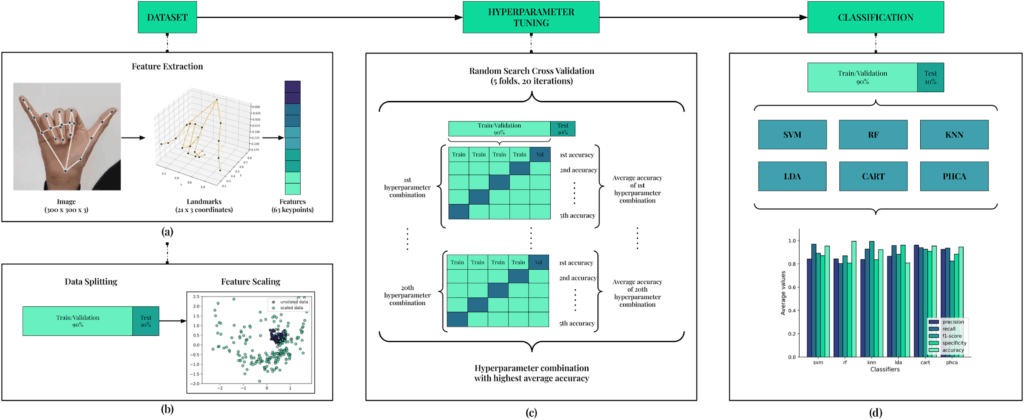
This research aims to improve recognition of Filipino Sign Language (FSL) letters, which is crucial for better communication in the growing deaf community.
Traditional deep learning methods are promising but have downsides, such as needing a lot of data and being difficult to interpret. This study introduces a new approach using techniques from computational topology, specifically the Persistent Homology Classification Algorithm (PHCA), which offers a simpler and more understandable alternative. By using PHCA, the researchers achieved high accuracy (99.31%) when recognizing FSL letters, with performance comparable to the top-performing Support Vector Machine (SVM), a machine learning algorithm used in sign language recognition.
An important advantage of PHCA is that it remains reliable even with variations or noisy data, showing strong stability. While PHCA struggles with signs that look similar, it still provides a promising solution for real-world applications, especially in areas like education, healthcare, and social services for the deaf community.
In conclusion, this study offers a fresh, robust alternative to current methods, showing that PHCA can be an important tool for improving sign language recognition systems, making them more transparent, efficient, and accessible for everyone. The research paves the way for further advancements and collaborations in accessible communication technology for the deaf.
Authors: Cristian B. Jetomo and Mark Lexter D. De Lara (both from the Institute of Mathematical Sciences, College of Arts and Sciences, University of the Philippines Los Baños)
Read the full paper: https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj-cs.2720
