Research
As the national university, we champion and support innovative research that addresses the country’s most pressing challenges.
26 Nov 2025
The service convenience of live broadcast shopping increases impulse buying by boosting perceived value and e-trust
With the growth of social media and social media marketing, it is natural that the hospitality and tourism industry should...
Read More25 Nov 2025
Time can only be accessed around a particular set of times
To measure time is to measure a clock. Historically, to ask “how long before harvest?” or “when will the festival...
Read More24 Nov 2025
The sedimentary rocks in the Central Cordillera, formed about 33–17 million years ago, came from volcanic rocks produced by an underwater volcanic region
Approximately 90% sedimentary rocks cover the Earth’s surface. These rocks are formed from the erosion and weathering of pre-existing rocks....
Read More21 Nov 2025
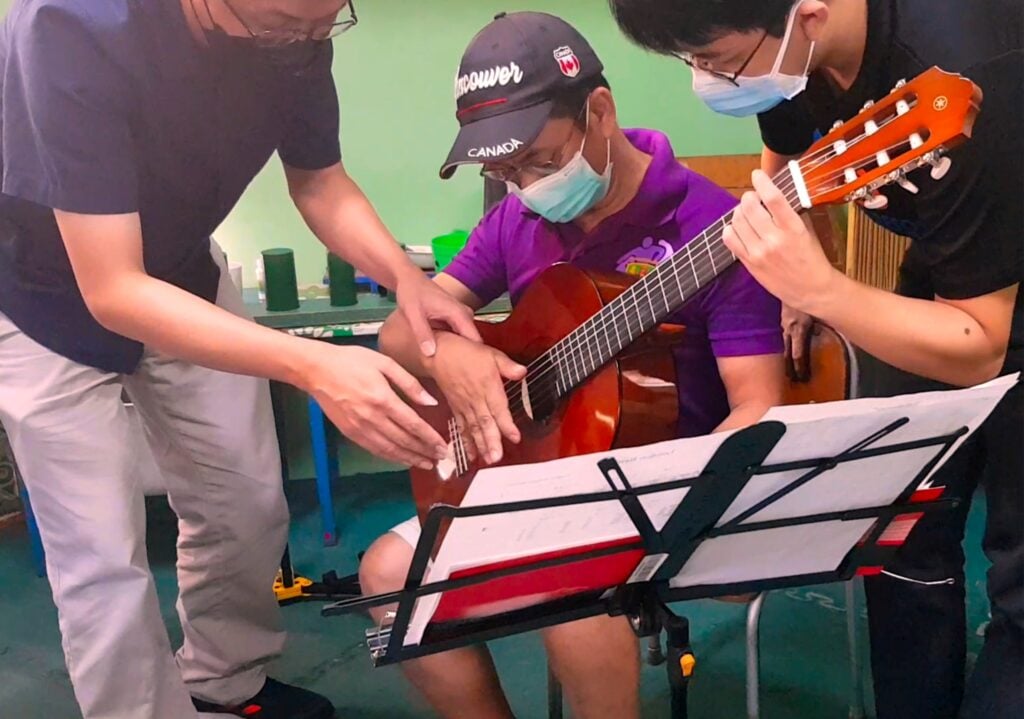
A guitar-based program resulted in improvements in hand function among stroke patients comparable to those from conventional therapy
This study aims to determine the effects of guitar lessons (intervention group) in comparison to conventional occupational therapy sessions (control...
Read More20 Nov 2025
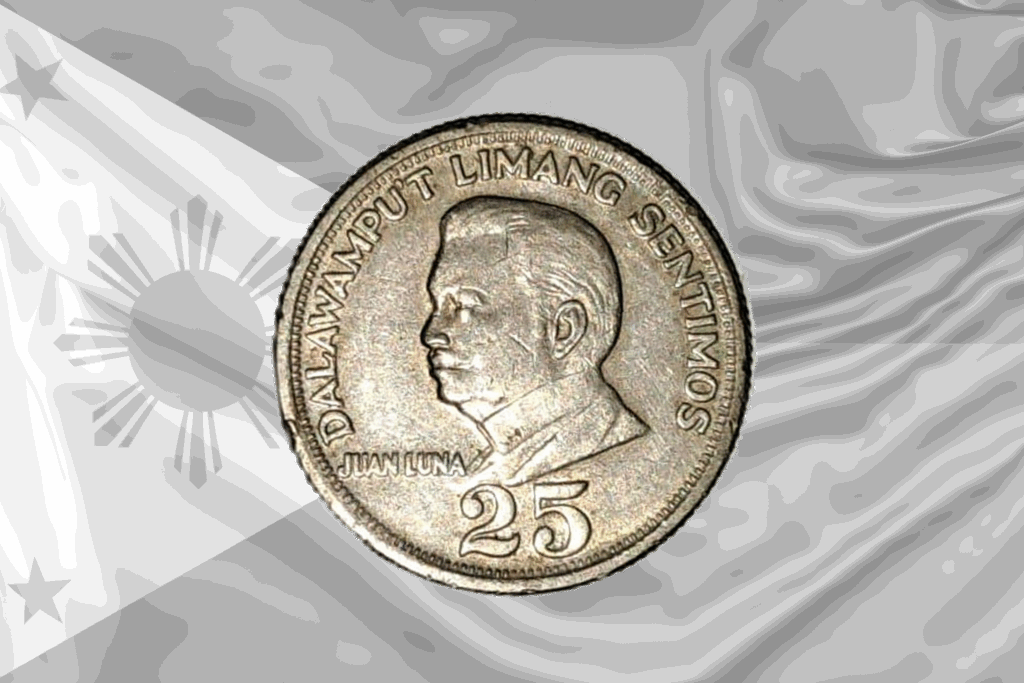
The commemoration of Juan Luna as a nationalist illustrates the dynamic and selective nature of public memory
This paper examines the creation and configuration of public memory in the Philippines by studying the case of Juan Luna....
Read More19 Nov 2025
Except for changes in the settings featuring women and men, gender portrayals in TV ads in 2010 and 2020 remained largely stereotypical
This study compares Philippine television advertisements in 2010 and 2020 to examine possible differences in gender representation. We conducted a...
Read More17 Nov 2025
Young adults face many personal conflicts rooted in the belief that personal gain at others’ expense is morally wrong
This study examined how Filipinos in their 20s use different moral discourses to negotiate their personal conflicts. Many conflicts centered...
Read More14 Nov 2025
Two in five individuals do not want to live in socialized housing, saying the units are too small, poor in quality, and still unaffordable
The most common housing concerns in the Philippines are affordability and supply. In response, the government divided the housing market...
Read More13 Nov 2025
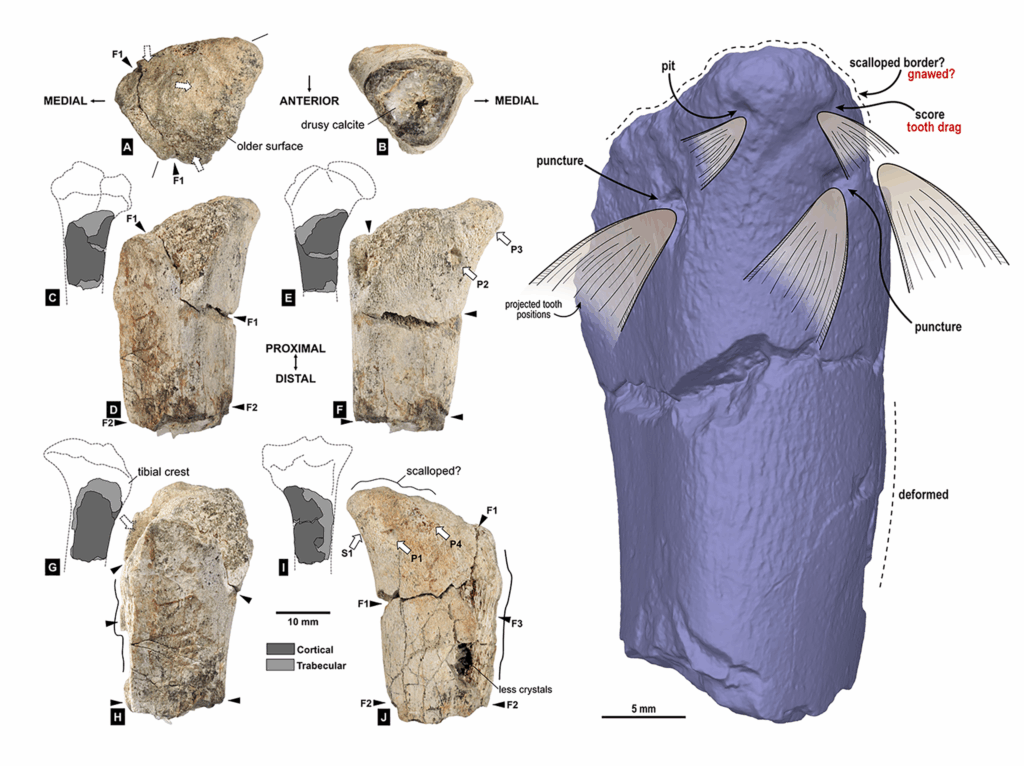
Evidence shows that during the Pleistocene, Luzon—long thought to lack native large mammalian carnivores—was home to a sizeable predator
Fossils are preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms, often turned to rock. Body fossils include parts like shells, teeth,...
Read More12 Nov 2025
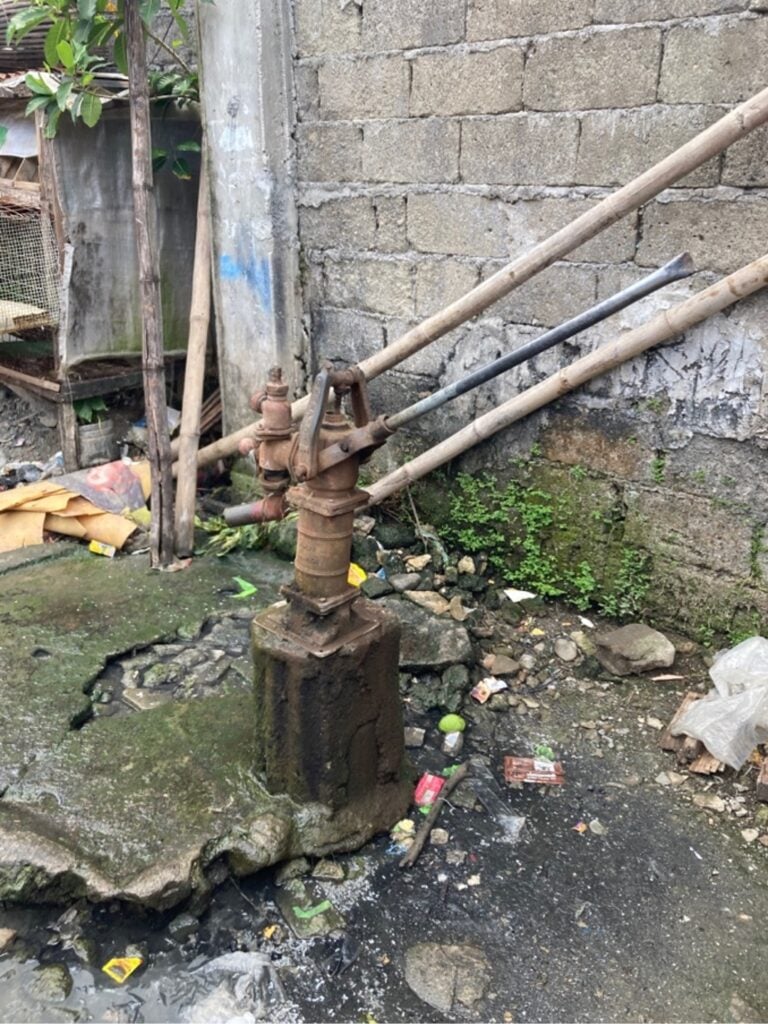
Some communities in Los Baños, Laguna still face challenges in accessing safe and clean drinking water
Due to rising costs or the inaccessibility of commercial water, many rural communities rely on artesian well (“poso”) water as...
Read More11 Nov 2025
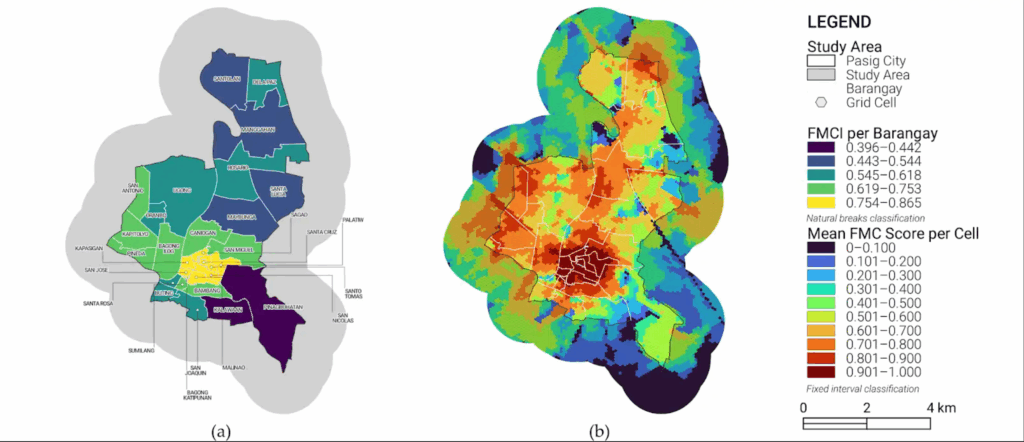
Walkability in urban cities should also consider the varying accessibility needs of people of all ages
Cities are meant to be places where people can easily access everything they need within a short walk or bike...
Read More24 Oct 2025
A new approach to volunteerism encourages schools to treat volunteer activities as long-term commitments
This research explored the motivations of students as a basis for deeper and more meaningful engagement among educational institutions in...
Read More